RRS Technical Section
Coil-Overs, Rack, & 3-Link Engineering
RRS has made available to engineers, certifiers, and signatories comprehensive engineering data files for the RRS coil-overs, GT rack, and 3-Link to suit classic Mustang, Falcon, Fairlane, and more.
The new Australian VSB14 compliance regulations mean all stressed components require finite element analysis. RRS has commissioned a certified, independent company to conduct the necessary modelling, mapping and load simulations.
If you’re building a classic Mustang, Falcon, Fairlane, Maverick, etc. and you want engineering certification, RRS has done the work and calculations.
For more information, feel free to look around our website or contact us.

Comparative Suspension Evaluation
This comparative study will look at the following:
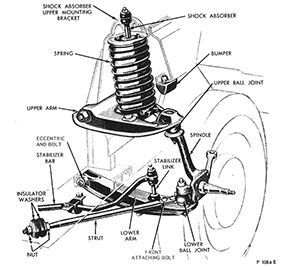
- Original Ford suspension
- Modified original Ford suspension
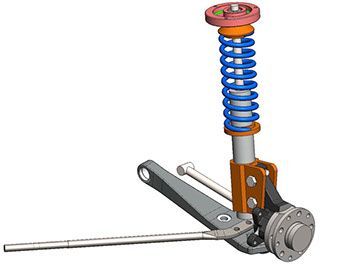
- RRS Strut conversion
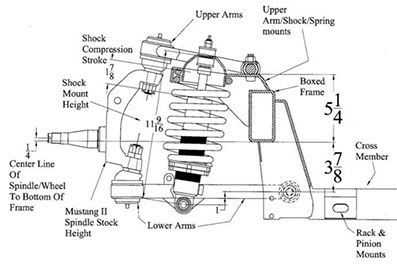
- Mustang II style front end
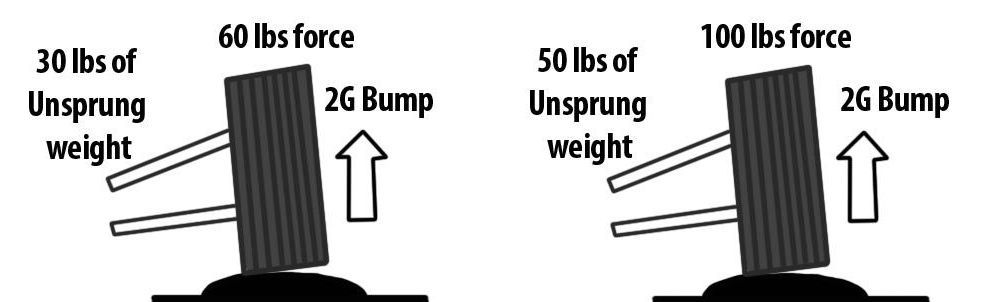
Unsprung Weight
Unsprung weight is the weight of the components hanging off the vehicle's suspension mounts such as wheels, rotors, control arms & shocks. The comparison will evaluate how the different suspension systems react to irregularities cause this mass to move.
0 points poor
1 point for average
2 points for excellent
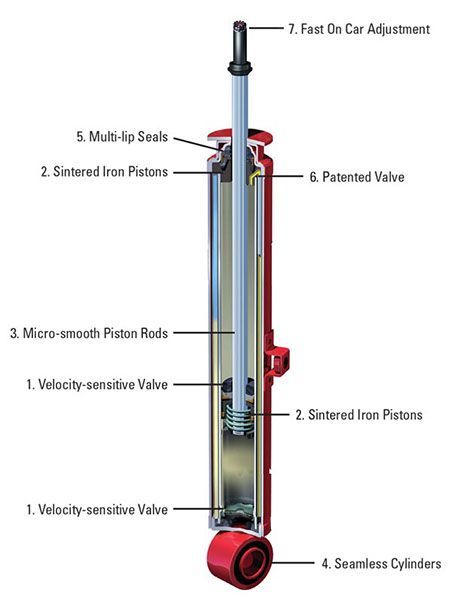
Shock Design
Shock design & adjustability play a key role in your suspension's ability to compensate for differing road surface conditions.
0 points poor (cheap)
1 point (good design, no adjustment)
2 points (good design & adjustability)
Spring Design
Your springs are affected by three main factors: manufacturing process, materials, and adjustability.
0 points poor OE replacement spring
1 point average economy spring
2 points excellent race engineered spring

Articulating Joints
Articulation joints are your suspensions ball joints & control arm bushings. These joints contribute to unsprung weight via friction & or resistance to movement.
0 points for poor (high friction)
1 point for average (low friction)
2 points for excellent (near-zero friction)
The Scores:
Original Ford Suspension:
Unsprung weight 0 , Motion ratio 0, Shock design 0, Spring design 0 , Articulation joints 0
TOTAL 0
Modified Ford:
Unsprung weight 0 , Motion ratio 0, Shock design 1 , Spring design 1 , Articulation joints 1
TOTAL 3
RRS Strut: Unsprung weight 2, Motion ratio 2, Shock design 2, Spring design 2, Articulation joints 2
TOTAL 10
Mustang II Style front end: Unsprung weight 1, Motion ratio 1, Shock design 2, Spring design 1, Articulation joints 1 TOTAL 6
Steering Geometry
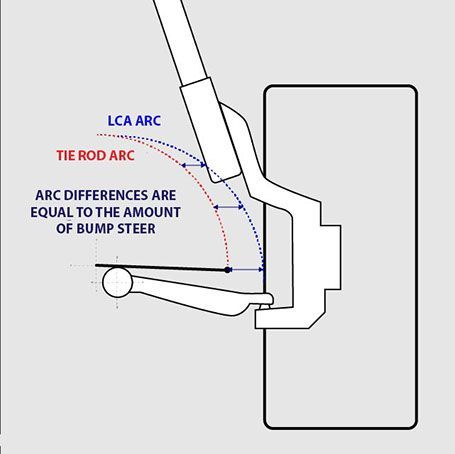
Bump steer is either a toe in or toe out effect as the suspension moves through its range of travel.
0 points for excessive bump steer, 1 point for low bump steer, 2 points for zero bump steer
Camber Gain
Camber gain is commonly accepted to be an increase in negative camber as the suspension moves from droop to full bump .It is desirable to have the appropriate amount of negative camber or negative camber gain, to match the amount of tyre sidewall deflection in order to maintain good tyre to road contact.(ideally full tread contact at full speed cornering)
0 points for positive camber gain
1 point for negative camber gain
2 points for tunable negative camber gain

Ackerman Angle
Is the angle determined principally by the location of the outer tie rod end in relation to the lower ball joint , so that the inside wheel on a turn will turn a proportionally smaller radius than the outside wheel ,to both match wheel base & wheel track .
0 points for incorrect Ackerman angle
1 point for good Ackerman angle
2 points for good and adjustable Ackerman angle (Ackerman angle can be adjusted by one of two ways:
a) adjustable outer tie rod end location
b) Adjustable inner tie rod end location
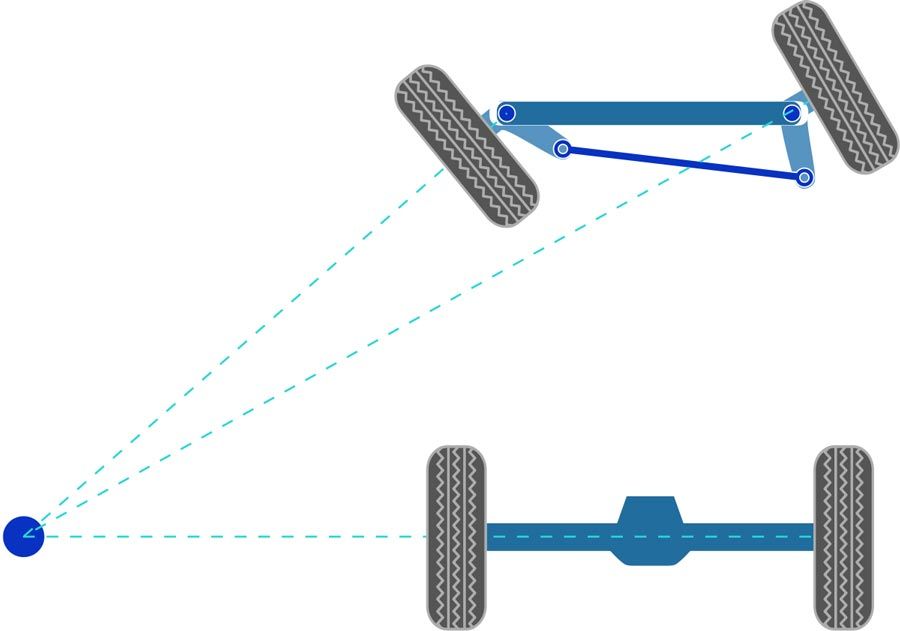
Steering Axis Inclination
Angle between vertical & a line connecting top & bottom pivots of a front suspension upright, seen from head on. Not to be confused with caster angle which is lean back angle on the top pivot behind the bottom pivot of a front upright, seen from the side of the car.
The amount of steering axis inclination is vital to suit modern radial design tyres.
0 points for incorrect steering axis inclination
1 point for acceptable steering axis inclination
2 points for acceptable & adjustable steering axis inclination
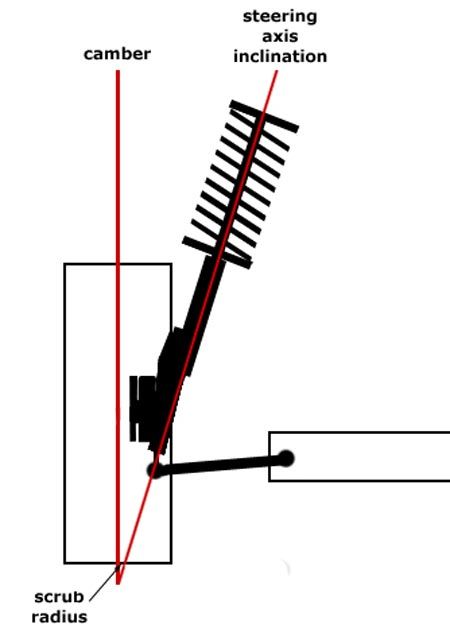
Caster Angle
Caster angle is the lean back angle of the top pivot behind the bottom pivot of a front upright, seen from the side of a car. The caster angle for modern tyres typically fall in the range of 2`-6` positive caster for a street car and 41/2- 81/2 positive caster for a race set up. The higher the caster angle the more self centering action will occur that helps a car run straight at high speeds, and will also pull the wheels back to straight ahead coming out of a corner.
0 points for lack of adjustment to reach 6`
1 point for lack of adjustment to reach 8.5`
2 points for an adjustment range from factory 1.5` to 8.5`
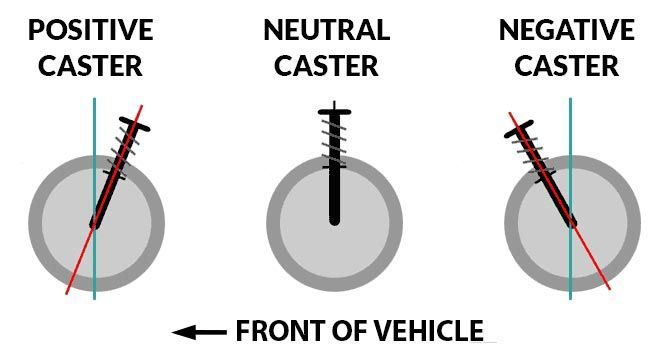
Jacking Effect
A jacking effect is created to either raise or lower the outside wheel opposite to the inside wheel to either increase body roll or decrease body roll. When body roll is decreased by this method a less stiff anti roll bar would be required.
0 points for a jacking effect that increases body roll
1 point for no jacking effect
2 points for a jacking effect that decreases body rollYour springs are affected by three main factors: manufacturing process, materials, and adjustability.
0 points poor OE replacement spring, 1 point average economy spring, 2 points excellent race engineered spring
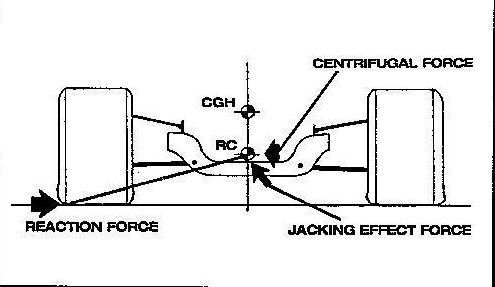
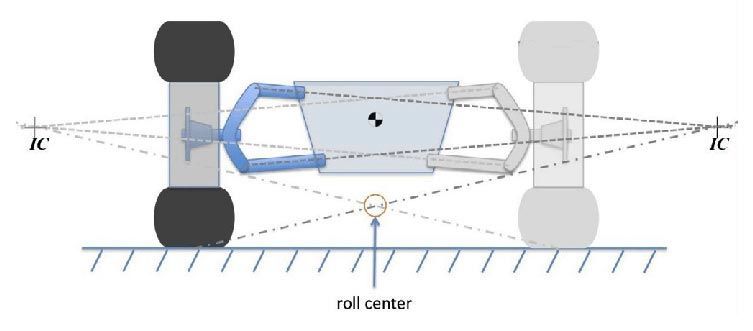
Roll Center Position (Instantaneous Roll Center Position)
This is the invisible moving point about which a vehicle is considered to rotate in a corner. Easy to plot in a static situation but far from easy once the vehicle is moving. The relationship between the roll center & center of gravity determine the roll moment .The roll moment is the leverage exerted by a vehicle attempting to roll,
0 points for either excessively high or low roll center positioning
1 point for either moderate, high or low roll center positioning
2 points for a tightly positioned roll center as low as possible before an increase in body roll is caused.
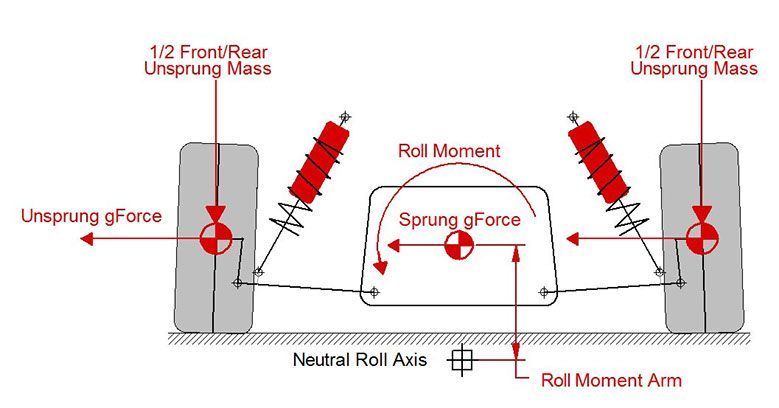
Roll Moment
Roll moment once calculated, helps determine how the sprung weight of the vehicle can be transferred to either end of the vehicle and can help determine the springs, roll bars strengths and the leverage with which they are applied.
0 points for a roll moment that will make a vehicle dangerous at high speeds corners
1 point for a roll moment that will make a vehicle stable in high speed corners but will lack cornering grip.
2 points for a roll moment that makes a vehicle stable in high speed corners and will increase grip
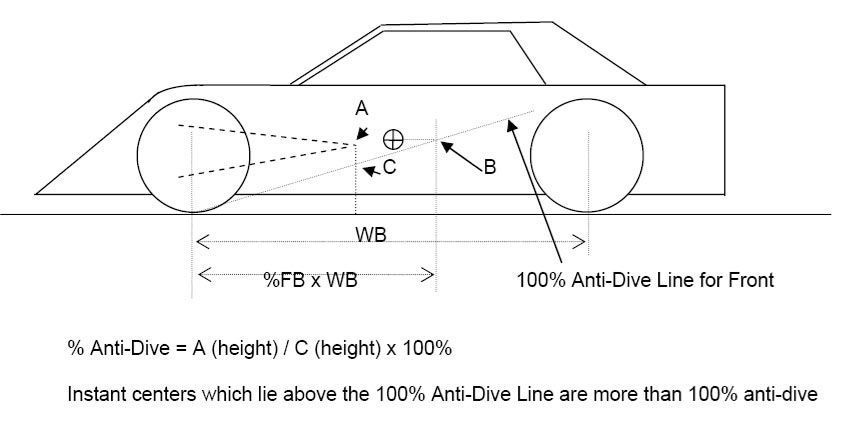
Anti Dive
Geometric method of reducing a vehicles tendency to nose dive under braking by tilting inboard suspension pick up points and or mounting the brake calipers front or rear of the axle center line
0 points for bad anti dive characteristics
1 point for moderate anti dive characteristics
2 points for optimum anti dive characteristics
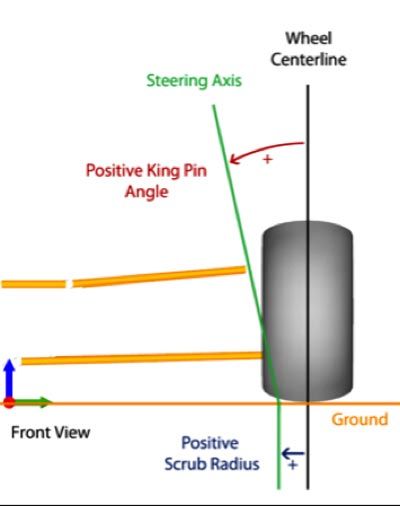
Scrub Radius
Scrub radius has been a loose term which is most commonly understood to apply to a radius of movement of the tyre contact patch on the horizontal plane .When there is too much movement caused by high scrub radius, typically the vehicle will either increase or decrease with wheel movement (Scrub radius is a result of a close relationship between wheel center line and suspension pivot points)
0 points for poor scrub radius characteristics
1 point for moderate scrub radius characteristics
2 points for optimum scrub radius characteristics
RRS strut : Bump steer 2 Camber gain 2 Ackerman angle 2 Steering axis inclination 2 Caster angle 2 Jacking effect 2 Roll centre position 2 Roll moment 2 Anti-dive 2 Scrub radius 2 TOTAL 20
OE Ford : Bump steer 0 Camber gain 0 Ackerman angle 0 Steering axis inclination 0 Caster angle 0 Jacking effect 0 Roll centre position 0 Roll moment 0 Anti-dive 0 Scrub radius 0 TOTAL 0
Modified Ford : Bump steer 0 Camber gain 1 Ackerman angle 0 Steering axis inclination 1 Caster angle 1 Jacking effect 0 Roll centre position 2 Roll moment 1 Anti-dive 0 Scrub radius 1 TOTAL 6
Mustang II Style :
Bump steer 1 Camber gain 2 Ackerman angle 0 Steering axis inclination 2 Caster angle 1 Jacking effect 1 Roll centre position 1 Roll moment 2 Anti-dive 2 Scrub radius 0 TOTAL 12
Installation Comparison
In reference to ease of installation and minimal tools and skills required for a safe performance outcome.
RRS strut : no fabrication and no specialty equipment required
OE Ford : no fabrication and no specialty equipment required
Modified Ford: no fabrication and no specialty equipment required
Mustang II Style: a large amount of fabrication and specialty equipment and skills required
Chassis Effects
Beaming & torsioning
Beaming is the bending of the vehicle end to end .Torsioning is the twist of the vehicle end to end
0 points for increasing beaming & torsioning
1 point for maintaining beaming & torsioning
2 points for decreasing beaming & torsioning

Loading & Fatiguing
Different suspension formats create loads in different suspension pivot points (where the sprung weight is carried). Fatiguing is typically a high stressed suspension pivot point or a reduction of the manufactures intended chassis integrity (OEM, uni-body chassis rely heavily on the integration of bolt on exterior body panels and frame welded panels)
0 points for changing the chassis design or incorrectly loading a pivot point
1 point for maintaining original chassis design and original loading pivot points
2 points for maintaining original chassis design and decreasing loading at pivot points
Space Options
Space in relationship to engine bay size (Mustang II can remove entire shock tower, RRS strut allows the option of shock tower notching to achieve an identical effect of useable space) and space in relation to the ease of serviceability of the suspension and steering components.
0 points for no improvement of space
1 point for improvement in space that requires additional modifications
2 points for improvement in space that does not require any additional modifications
Weight
The gross vehicle mass ideally for any performance application should be as light as possible with no loss of chassis integrity
0 points for increased weight
1 point for maintaining weight
2 points for decreasing weight
Chassis Integrity
Chassis integrity is affected by age, original design, modifications and skill of the tradesman who carries out the modifications. This will determine the duty cycle (lifespan) and safety of the vehicle
0 points for decreasing chassis integrity (the likely hood of failure)
1 point for maintaining chassis integrity
2 points for increasing chassis integrity
RRS strut with notch kit: Beaming & tensioning 2 Loading & fatigue point 2 Space 2 Weight 2 Chassis integrity 2 Total 10
OE Ford: Beaming & tensioning 1 Loading & fatigue point 1 Space 0 Weight 1 Chassis integrity 1 Total 4
Modified Ford: Beaming & tensioning 1 Loading & fatigue point 1 Space 0 Weight 1 Chassis integrity 1 Total 4
Mustang II style:
Beaming & tensioning 0 Loading & fatigue point 0 Space 1 Weight 2 Chassis integrity 0 Total 3
Cost analysis
Cost analysis can be extremely deceiving .While a product may be higher priced to purchase than others , others may require additional purchases or labor costs .Therefore costs analysis can be broken down into the following categories.
Dollars versus performance
Basically bang for buck .When the product is stacked up against the competition does it offer a vast difference that justifies the cost?
0 points for dollars spent and no performance increase
1 point for dollars spent and moderate performance increase
2 points for dollars spent and substantial performance increase
Dollars versus completeness
Is it all there? Or are there hidden extras not revealed in the asking price
0 points for dollars spent and not complete
1 point for dollars spent and is complete
2 points for dollars spent and comes with additional components
Dollars versus additional labour costs
If professionally installed what the labour cost will be versus the ability to perform the modifications at home.
0 points for dollars spent and added labour costs
1 point for dollars spent and no added labour costs
2 points for dollars spent and decreased labour costs
Dollars versus maintenance costs
Are replacement parts easy to get for the product?
0 points for dollars spent and high maintenance costs
1 point for dollars spent and no additional maintenance costs
2 points for dollars spent and reduced maintenance costs
Dollars versus versatility
Can the system be upgraded over time?
0 points for dollars spent and no versatility
1 point for dollars spent and minimal versatility
2 points for dollars spent and maximum versatility
RRS strut: Dollars versus performance 2 Dollars versus completeness 2 Dollars versus added labour 2 Dollars versus maintenance 2 Dollars versus versatility 2 Total 10
OE Ford: Dollars versus performance 0 Dollars versus completeness 2 Dollars versus added labour 2 Dollars versus maintenance 2 Dollars versus versatility 0 Total 6
Modified Ford: Dollars versus performance 1 Dollars versus completeness 2 Dollars versus added labour 2 Dollars versus maintenance 2 Dollars versus versatility 0 Total 7
Mustang II Style:
Dollars versus performance 1 Dollars versus completeness 0 Dollars versus added labour 0 Dollars versus maintenance 0 Dollars versus versatility 2 Total 3

Warranty & Safety
In the automotive after market industry, unlike OEM, products can be sold and manufactured without any quality controls and evaluation of the safety of the vehicle's modification.
Therefore, if you are purchasing an automotive after market product to modify your vehicle, make sure it engineered tested, and it is street legal in your jurisdiction.
RRS HO2 Coil overs, brake systems, rack and pinion steering kits, under dash brake boosters, and 3 link rear suspension systems have been tested, and the tests validated by independent bodies, making RRS products internationally street legal.
RRS Guarantee and Warranty
RRS products have undergone rigorous engineering analysis and testing by some of the Worlds toughest Government authorities and engineering signatories , which enables RRS to standby its products with full 5 year unlimited kilometre warranty as if you are buying an OE replacement part for your road vehicle .No other steering system meets RRS high standards & guarantee.